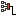Aionios=
The New Testament in Modern Speech, by Dr. R. F. Weymouth
Eternal: Greek: “aeonion,” i.e., “of the ages.” Etymologically this adjective, like others similarly formed, does not signify “during,” but “belong to” the aeons or ages."
The Interpreter’s Dictionary of the Bible (vol. IV, p. 643)
Time: The O.T. and the N.T. are not acquainted with the conception of eternity as timelessness. The O.T. has not developed a special term for “eternity.” The word aion originally meant “vital force,” “life,” then “age,” “lifetime.”
Elliot’s Commentary on the Whole Bible (Matt. 25:46)
Everlasting punishment–life eternal. The two adjectives represent the same Greek word, aionios-it must be admitted that the Greek word which is rendered “eternal” does not, in itself, involve endlessness, but rather, duration, whether through an age or succession of ages, and that it is therefore applied in the N.T. to periods of time that have had both a beginning and ending (Rom. 16:25).
Hasting’s Dictionary of the New Testament (Vol. I, p. 542, art. Christ and the Gospels)
Eternity. There is no word either in the O.T. Hebrew or the N.T. Greek to express the abstract idea of eternity. (Vol. III, p. 369): Eternal, everlasting-nonetheless “eternal” is misleading, inasmuch as it has come in the English to connote the idea of “endlessly existing,” and thus to be practically a synonym for “everlasting.” But this is not an adequate rendering of aionios which varies in meaning with the variations of the noun aion from which it comes. (p. 370):
The chronoios aioniois moreover, are not to be thought of as stretching backward everlastingly, as it is proved by the pro chronon aionion of II Tim. 1:9; Titus. 1:2. (Note: pro chronon aionion means “BEFORE times eonian.” Since this Scripture tells us that there was time “before” eonian, eionian cannot possibly mean eternal, for nothing can be “before” eternity.)
The large Catholic Bible dictionary, The Encyclopedic Dictionary of the Bible (p. 693)
ETERNITY: The Bible hardly speaks of eternity in the philosophical sense of infinite duration without beginning or end. The Hebrew word olam, which is used alone (Ps. 61:8; etc.) or with various prepositions (Gen. 3:22; etc.) in contexts where it is traditionally translated as ‘forever,’ means in itself no more than 'for an indefinitely long period." Thus me olam does not mean ‘from eternity’ but ‘of old’ Gen. 6:4; etc.). In the N.T. aion is used as the equivalent of olam. (Note: even the Catholic translators of The Jerusalem Bible and The New American Bible have failed to heed the scholarship of their own Catholic authorities.)
Dr. R. F. Weymouth, a translator who was adept in Greek, states in The New Testament in Modern Speech (p. 657)
Eternal, Greek aeonion, i.e., of the ages: Etymologically this adjective, like others similarly formed does not signify, “during” but “belonging to” the aeons or ages.
Dr. Marvin Vincent, Word Studies of the New Testament (Vol. IV, p. 59).
The adjective aionios in like manner carries the idea of time. Neither the noun nor the adjective in themselves carries the sense of “endless” or "everlasting.’ Anionios means enduring through or pertaining to a period of time.
Dr. F. W. Farrar, author of The Life of Christ and The Life and Word of St. Paul, as well as books about Greek grammar and syntax, writes in The Eternal Hope (p. 198)
In Dr. Farrar’s book, Mercy and Judgment, (p. 378)
“Since aion meant ‘age,’ aionios means, properly, ‘belonging to an age,’ or ‘age-long,’ and anyone who asserts that it must mean ‘endless’ defends a position which even Augustine practically abandoned twelve centuries ago. Even if aion always meant ‘eternity,’ which is not the case in classic or Hellenistic Greek- aionios could still mean only ‘belonging to eternity’ and not 'lasting through it.”
The Interpreter’s Dictionary of the Bible, (Vol. 4, p. 641)
“The O.T. and the N.T. are not acquainted with the concept of eternity as timelessness.” Page 655: “The O.T. has not developed a special term for eternity.” Page 645: “The use of the word aion in the N.T. is determined very much by the O.T. and the LXX. Aion means long, distant, uninterrupted time. The intensifying plural occurs frequently in the N.T. but it adds no new meaning.”
Dr. Edward Plumptre, an eschatologist
“I fail to find, as is used by the Greek Fathers, any instance in which the idea of time duration is unlimited.”
Time and Eternity by G. T. Stevenson, (p. 63)
“Since, as we have seen, the noun aion refers to a period of time it appears, very improbable that the derived adjective aionios would indicate infinite duration, nor have we found any evidence in Greek writing to show that such a concept was expressed by this term.”
Professor Herman Oldhausen, German Lutheran theologian
“The Bible has no expression for endlessness. All the Biblical terms imply or denote long periods.”
Professor Knappe of Halle wrote
“The Hebrew was destitute of any single word to express endless duration. The pure idea of eternity is not found in any of the ancient languages.”
An Alphabetical Analysis by Charles H. Welch (Editor of The Berean Expositor and a man well versed in Greek), (Vol. 1, p. 279)
“Eternity is not a Biblical theme.” (Vol. 1, p. 52), “What we have to learn is that the Bible does not speak of eternity. It is not written to tell us of eternity. Such a consideration is entirely outside the scope of revelation.”
Dr. Mangey, a translator of the writings of Philo, says
“Philo did not use aionios to express endless duration.”
The Complete Works of Falvius Josephus.
Josephus obviously did not consider anionios to be “everlasting,” seeing that he uses the word to represent the period of time between the giving of the law of Moses and that of his own writing [clearly not an eternity] . He also assigns aionios to the period of imprisonment of the tyrant John by the Romans [clearly he was not imprisoned for an eternity] , and also for the period during which Herod’s temple stood [since Herod’s temple was not even standing at the time Josephus wrote, it too proves that Josephus did not mean ‘eternity’ when he wrote ‘aionios’] .
Saint Gregory of Nyssa speaks of anionios diastema
“an eonian interval.” How many intervals do you know of that are “endless” or “eternal?”
Saint Chrysostum, in his homily on Eph. 2:1-3
“Satan’s kingdom is aeonian; that is, it will cease with the present world.”
Saint Justin Martyr, in the Apol. (p. 57)
Used the word aionios repeatedly: aionion kolasin…all ouchi chiliontaete periodon, “eonian chastening but a period, not a thousand years,” or as some translate this clause “but a period of a thousand years only.” Hence, to Justin Martyr, aionios was certainly not “endless.”
Dr. O.B. Jenkins
Time or Character, The Ages or A Time Sequence in <em>aionios</em>: How Words "Mean" in Greek and English